Immunotherapy in the application of the research and treatment
Aline, when people think of immunotherapy of cancer, but in fact, the application of immune therapy is much more widely.In addition to cancer, what do you think of it in the field of which the most potential?
In the applications of cancer, we use immunotherapy to transfer the patient's own immune cells to attack the cancer cells, in the beginning, that is, a century ago, cancer immunotherapy face doubt, now already had more than one kind of "cancer vaccine" approved for clinical use, thus, this is an amazing achievement.
In spite of this, but most of the approved immunotherapy has tried to do exactly the opposite, which hinder the patient's cells under attack.In some cases, the immune cells will attack them shouldn't be the object of the attack.In this regard, the most common application of immunotherapy is slow autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes progression.
There are some cases, the immune cells will overreact.Anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, for example, we use to relieve and inhibiting cytokine storm, because cytokine storm is leading to new crown infection such as pneumonia and the cause of many serious complications such as traumatic spinal cord injury.
Sometimes, we want to cheat the immune cells, making them ignore or it is better to accept some useful treatment - for example, is one of the most common, promote cell and organ transplantation by using immunosuppressant.In addition, it is worth noting that the body of some of the long-term treatment of drug resistance there are likely to be immune, composition, and design many studies attempt to these drugs, make it to evade immune cells detection.
Although immunotherapy has existed for more than a century, but in the past few years, the therapy has experienced great development.Can you list some of the milestones?
If the green tea has a natural anti-inflammatory and immune cells such as modified features into consideration the herbal remedies, immunotherapy has been in existence for thousands of years, so to speak.In the early 19th century, we in the separation and identification of these herbs to make real progress, the active ingredient, which developed the first generation of modern immunomodulatory drugs.Soon after, the modern pharmaceutical companies began to appear, they have developed a variety of chemically modified natural compound method, to improve the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of these compounds, one of the most worth mentioning is the 1897 aspirin.In addition, around the same time (1891), also for the first time in a kind of using inactivated bacteria to stimulate immune cells attack the tumor cancer vaccines.Following a series of more specific drugs and therapy on the role model, but it must be mentioned is that the next major milestone is developed in the 1960 s used to slow the immunosuppressive drugs of graft rejection reaction.A few years later, found that many of these drugs in patients with autoimmune diseases is also effective.To this end, the U.S. food and drug administration (FDA) in 1986 approved the first monoclonal antibody drug Orthoclone OKT3.Moreover, although the cell therapy was acquired in early attempt, and in many diseases in preclinical models is a success, but it wasn't until recently approved for use in clinical application.For example, more than a decade ago, Sipuleucel -t approved for use on a patient's own immune cells to the decoration, in order to attack cancer cells.In addition, it is also a landmark, in 2017, for the first time in two kinds of engineering immune cells (CAR) therapy for cancer treatment application approval.
The role of imaging in immune therapy? What are those?
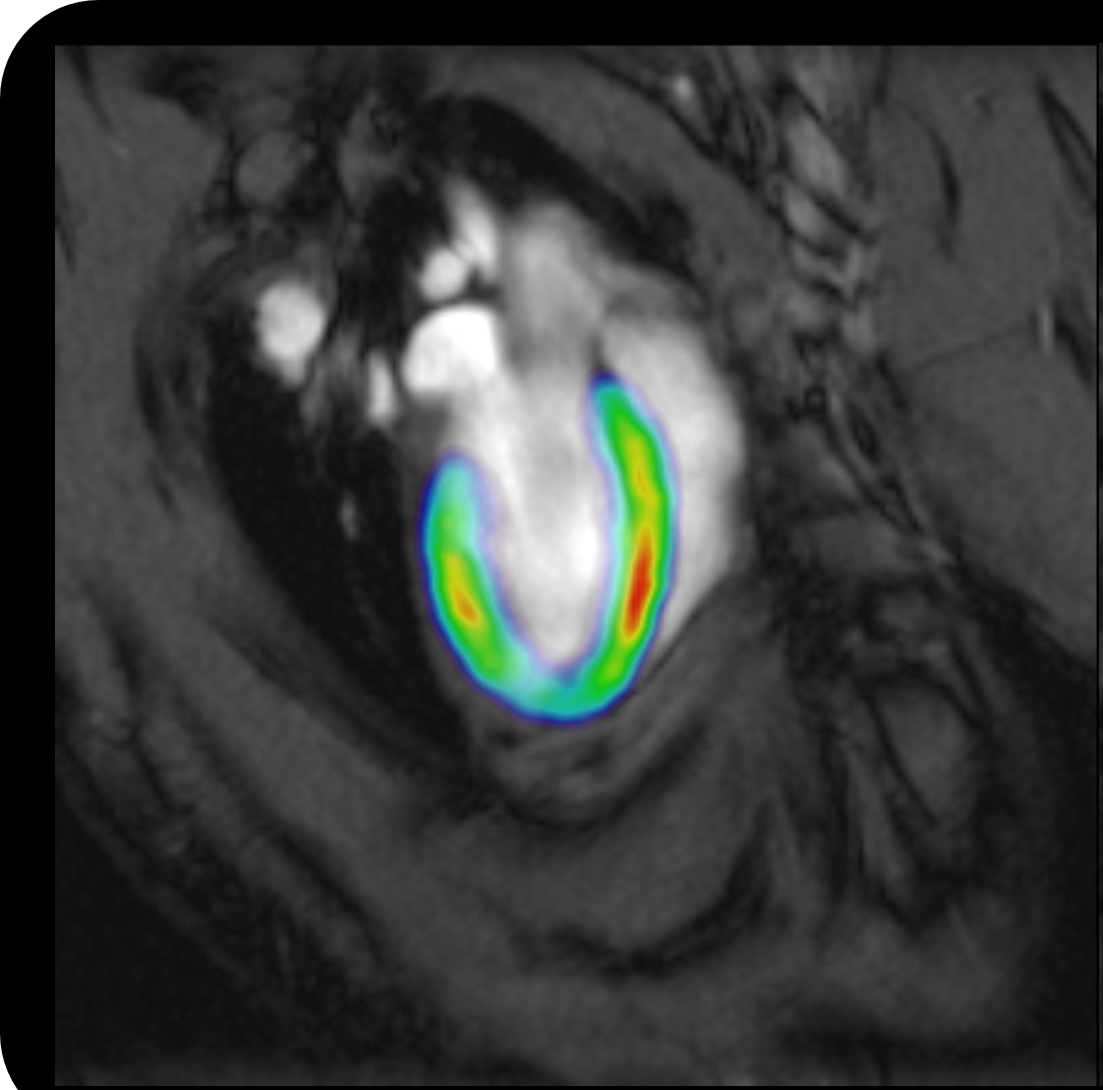
In the clinical, imaging in the application of immunotherapy mainly including check whether the disease is deteriorating, for example, check whether any new patients with multiple sclerosis lesions, or whether the cancer patients lesions.This is because the existing imaging method to cause the disease of molecules and cells is highly sensitive.In some cases, we need to use metal reagent to "tag" of immune cells, to track these cells.In this way, we can find out how immune cells in the body move, how to obtain the corresponding clues to know whether need to attack.In spite of this, we can't through this method to find the clues to what is, and how immune cells based on these clues to react to what response (or).
At present, we can use targeted imaging probe, through more specific markers for monitoring the reaction of immune cells.These probes have been used to monitor associated with inflammation and immune cell activation/deactivation of biological processes, for example, from glucose metabolism, zhuo type to peripheral benzodiazepine receptors expression, the corresponding probe FDG (fluorine deoxidization glucose) and TSPO (translocation) is currently in clinical trials for monitoring cancer immunotherapy and inflammatory disease progression of one of the most popular molecular imaging biomarkers.
Imaging in immunotherapy study what role?
For preclinical studies, we have developed a number of imaging to monitor treatment process itself - whether it is a small molecule drug therapy or cell therapy.We use these techniques to understand drug is we hope direction, namely in diseased tissues or immune cells, rather than for other possible side effects of organs and tissues.We have successfully demonstrated that the same as the candidate therapies targeted molecular imaging probes can be predicted the benefit of these treatments and is a powerful tool to judge the effect of the treatment.Much of the new progress around to positron emission tomography technology, this is a used to detect the corresponding probe therapy or related radiation imaging technology.However, there are more and more of the probe is in development or transferred to be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging technology, this will help us greatly extend these imaging biomarkers in patients with groups of accessibility in the future.
Your study objects including immune therapy not only, still include biomarkers.In this context, both why so important?
My exploration of imaging biomarkers from me in the development of therapy research.During the period of graduate studies, I try to find a specific imaging biomarkers, so that on the basis of the biomarkers to assess how I developed by immunotherapy in patients work/play what role.In preclinical studies, there are many tools can help scientists better understand the disease and its treatment, but these tools and can not be used in patients.A result we are unable to quickly complete the candidate therapies into and from the multiple choices approved therapies.If you have enough time, we will be able to confirm a therapy is effective for patients.However, for those who can benefit from immunotherapy of cancer patients, patients with autoimmune diseases or transplant patients, time is pressing.In our current decision within the time required for, their quality of life, the great changes may by then, they may not have the condition to accept alternative or combination therapy should be effective.In addition, it is difficult for us to find out the reason that the particular treatment doesn't work.I believe that the information provided by the imaging will help simplify the medical decision making, we find therapy will benefit patients, and to determine whether a specific treatment is invalid faster.
For those who can benefit from immune treatment of patients, time is pressing.
I believe that the information provided by the imaging will help us to simplify the medical decision making.
Aline Dr Thomas
Dr Thomas is now the Johns Hopkins university school of medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, an assistant professor of radiology.Before that, she was at the Massachusetts institute of technology (Cambridge, Massachusetts) both biological and chemical engineering degree, and at northwestern university, Evanston, Illinois) for biomedical engineering doctoral degree (major in polymer biomaterials).In addition, she is still in Georgia institute of technology (Atlanta, Georgia) accepted the immune engineering postdoctoral training, and accepted the molecular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at Johns Hopkins university postdoctoral training.Her research project combined with biological materials, calculation method and molecular imaging to develop new immune therapy and used to evaluate the immune therapy can transform imaging biomarkers.